(2024/04/06更新) 因應React在18後更新了許多不同的語法,更新後的教學之後將陸續放在 新的blog 中,歡迎讀者到該處閱讀,我依然會回覆這邊的提問
很多時候,我們的state必須要透過HTTP Request從後端取得。然而發送Request常用的fetch或是axios是非同步的。雖然我們可以透過以下方式把資料送進去Redux:
fetch( "URL", {
method: "GET"
})
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => {
dispatch({type:"TYPE", payload: {data}});
})
.catch(e => {
/*發生錯誤時要做的事情*/
}
)
但最理想的狀況還是讓這個fetch的過程被模組、抽象化,也就是不應該還要讓UI繪製程式還要自己去call fectch API。我們希望UI繪製程式只需要呼叫一個函式,從fetch到更新Redux的這串過程都會完成。
不論是在Flux,還是傳統的MVC、MVP、MVVM觀念下,都希望把資料處理的程式抽離UI繪製的程式,而不是讓兩者混雜在一起
講白一點,我們的流程本來是:
現在我們希望流程改成這樣:
一般會把2這種在本來行為之間(1和3)的加工過程稱為middleware(中介層)。
Redux-Thunk就是一個簡化Redux處理非同步事件的中介層套件。它的運作流程是這樣的,基本上就跟我們剛剛說的差不多:
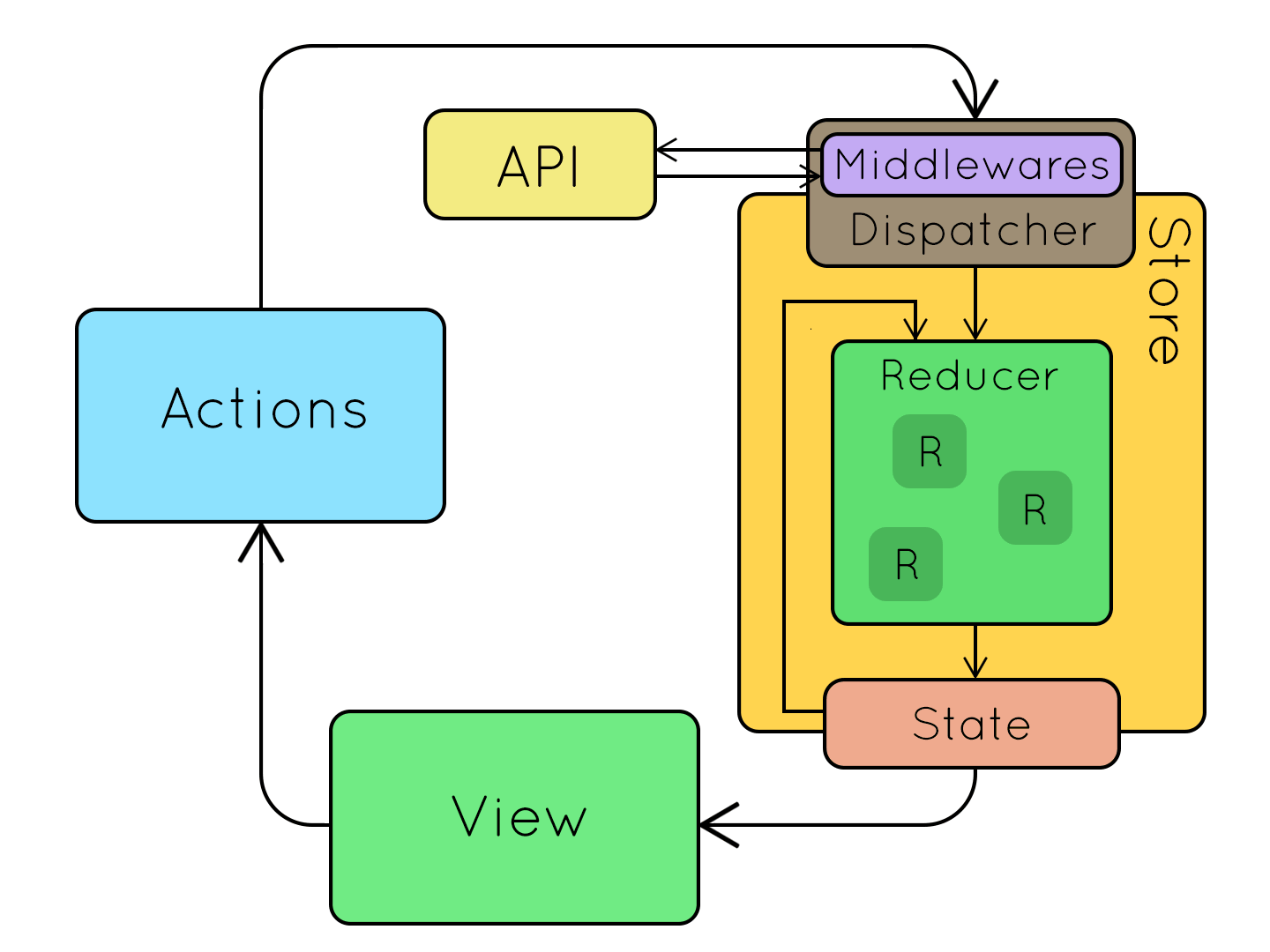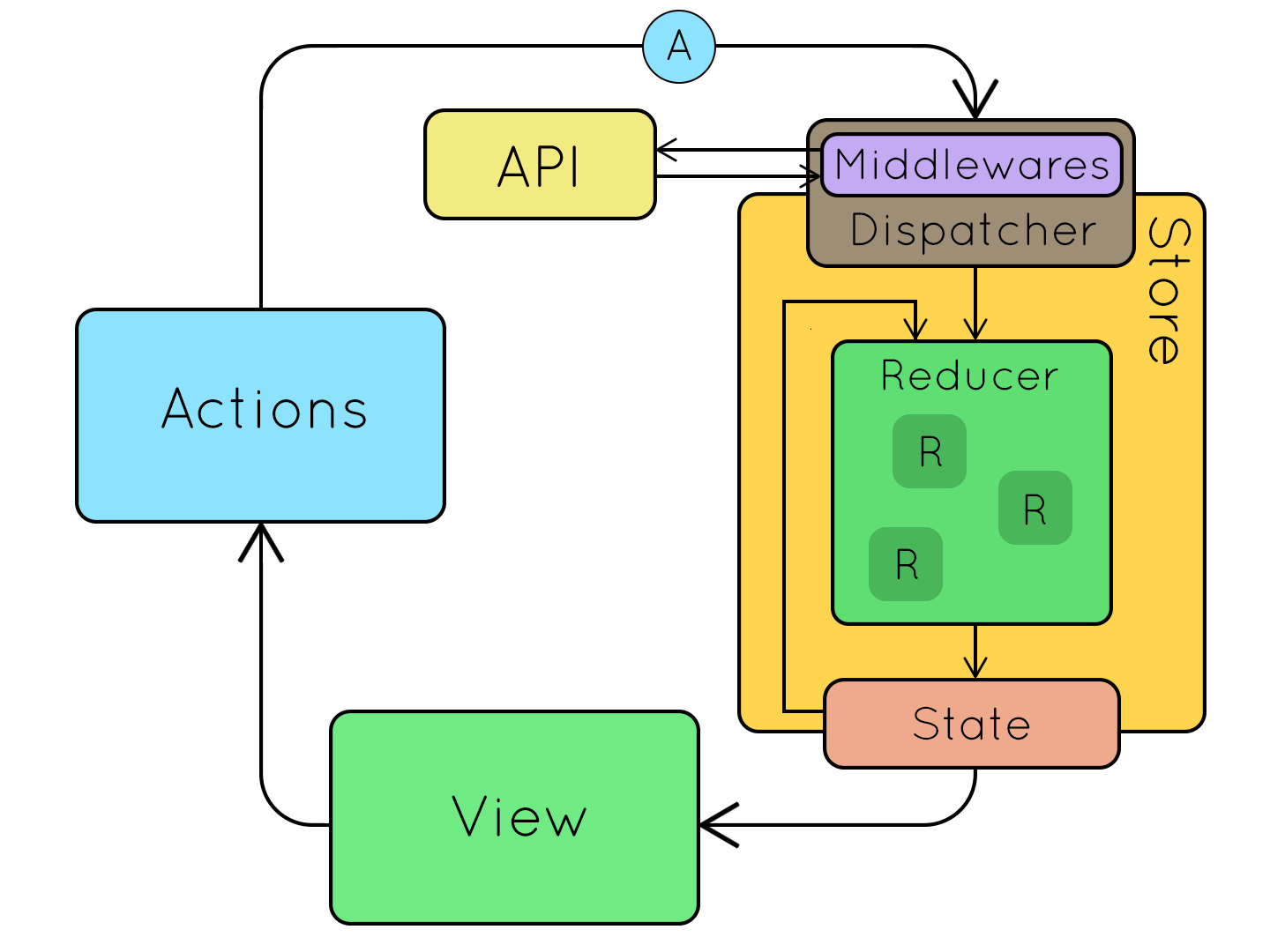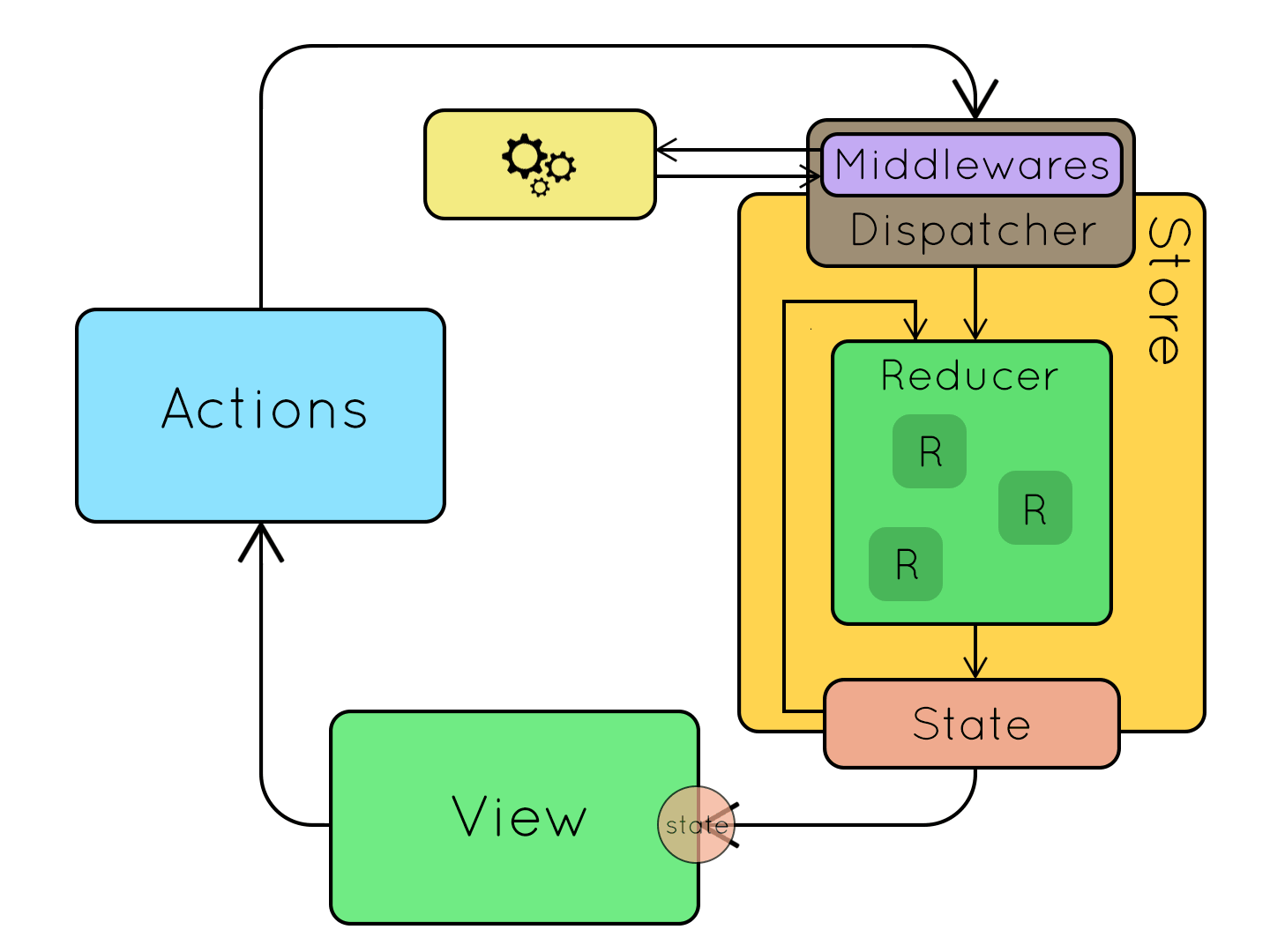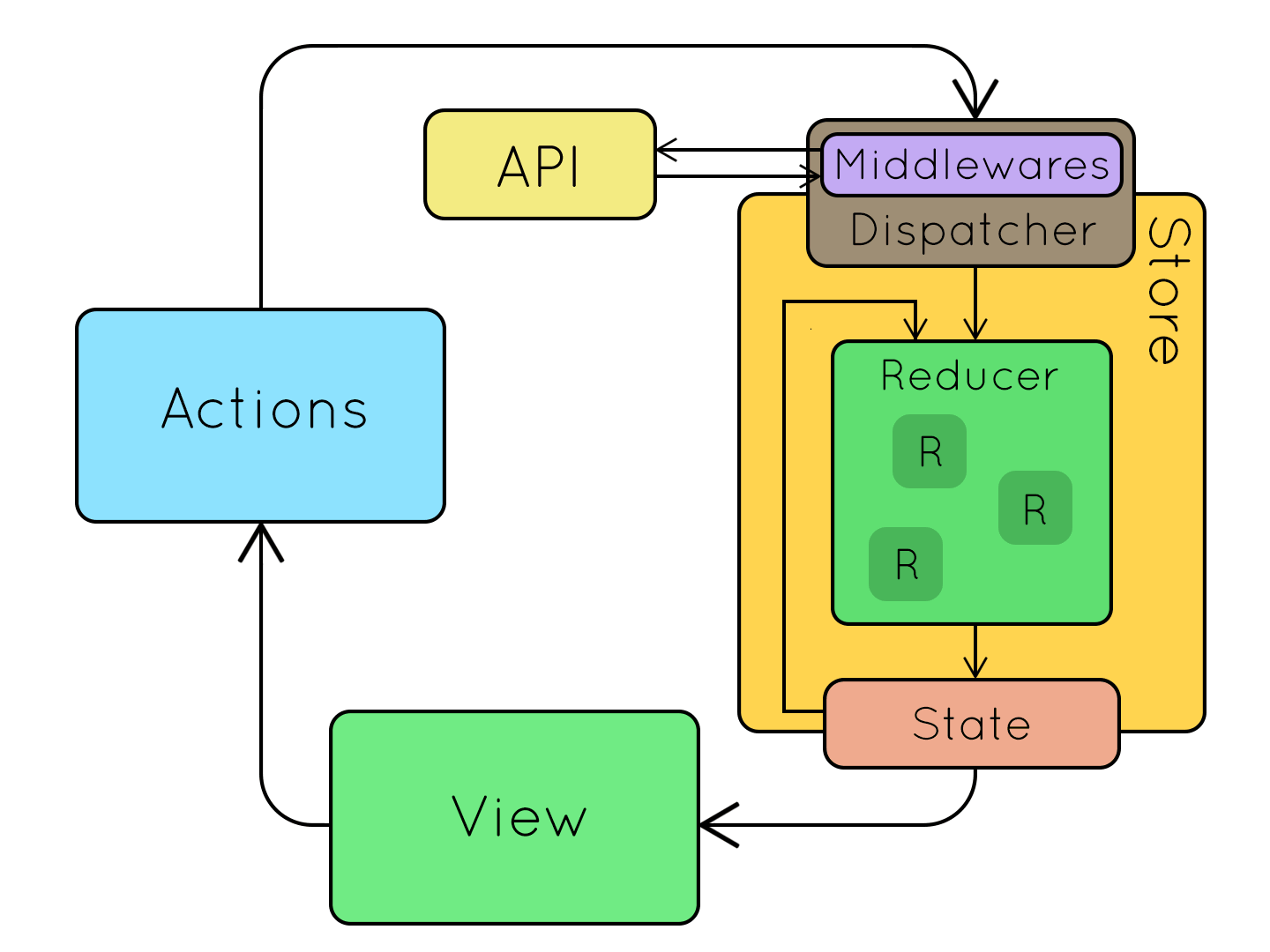
上圖來源。
接下來我們會實際操作一次Redux-Thunk,試著把MenuItem的資料改成從後端取得。資料會用我放在自己github的台灣的縣市列表JSON檔。
{
"cityList":[
"臺北市",
"基隆市",
"新北市",
(略......)
]
}
請打開terminal,輸入:
npm install redux-thunk --save
一般會在這裡以變數統一管理action字串。不過這裡我們先拿來放等等要定義的fetch
在src/model/action.js中,定義一個函式,把item改成fetch函式得到的資料。Redux-Thunk會把dispatch函式當成函式的參數傳入。我們則要在非同步事件結束後再次呼叫dispatch,給予對應的action和payload。
因為現在我們的reducer還沒有這種一次修改所有資料的action,我們先加一個SET_ITEM,等等再加回reducer中。
export const fetchCityItem = () => {
return (dispatch) => {
fetch( "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JiaAnTW/mask/master/dist.json", {
method: "GET"
})
.then(res => res.json())
.then(data => {
dispatch({
type: "SET_ITEM",
payload: {itemNewArr: data["cityList"]}
});
})
.catch(e => {
console.log(e);
})
};
};
Redux提供了applyMiddleware這個函式來讓我們安裝middleware到Redux中。用法是將applyMiddleware(中介層1,中介層2,...)放在createStore的第二個參數中。
現在,請引入Redux-Thunk的thunk和Redux的applyMiddleware,並加入我們的store中:
import {createStore, applyMiddleware } from "redux";
import {itemReducer} from "./reducer.js";
import thunk from "redux-thunk";
const itemStore = createStore(itemReducer,applyMiddleware(thunk));
export {itemStore};
這樣使用Redux-thunk的架構就完成了。
const initState = {
menuItemData: [
"Like的發問",
"Like的回答",
"Like的文章",
"Like的留言"
],
};
const itemReducer = (state = initState, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'ADD_ITEM': {
const menuItemCopy = state.menuItemData.slice();
return { menuItemData: [action.payload.itemNew].concat(menuItemCopy) };
}
case 'SET_ITEM': {
return { menuItemData: action.payload.itemNewArr };
}
case 'CLEAN_ITEM': {
return { menuItemData: [] };
}
default:
return state;
}
};
export {itemReducer};
觸發Redux-Thunk的方式,是在需要的地方呼叫
dispatch( 剛剛定義的非同步函式() );
也就是你可以在src/page/MenuPage新增一個按鈕:
<button onClick={()=>{
dispatch(
fetchCityItem()
);
}}>抓取並修改menuItem</button>
按下去之後,Redux就會根據我們剛剛定義的內容,先執行發送Http Request,等資料回來,才執行dispatch,把action和剛剛放入payload的縣市資料丟到reducer去更新。
import React, { useState, useReducer,useMemo,useEffect} from 'react';
import useMouseY from '../util/useMouseY';
import MenuItem from '../component/MenuItem';
import Menu from '../component/Menu';
import { OpenContext } from '../context/ControlContext';
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
import { fetchCityItem } from '../model/action';
const reducer = function(state, action){
switch(action.type){
case "SWITCH":
return !state;
default:
throw new Error("Unknown action");
}
}
const MenuPage = () =>{
const [isOpen, isOpenDispatch] = useReducer(reducer,true);
const menuItemData = useSelector(state => state.menuItemData);
const dispatch = useDispatch();
let menuItemArr = useMemo(()=>menuItemData.map((wording) => <MenuItem text={wording} key={wording}/>),[menuItemData]);
return (
<OpenContext.Provider value={{
openContext: isOpen,
setOpenContext: isOpenDispatch
}} >
<Menu title={"Andy Chang的like"}>
{menuItemArr}
</Menu>
<button onClick={()=>{
dispatch({
type: "ADD_ITEM",
payload: {itemNew:"測試資料"}
});
}}>更改第一個menuItem</button>
<button onClick={()=>{
dispatch(
fetchCityItem()
);
}}>抓取並修改menuItem</button>
</OpenContext.Provider>
);
}
export default MenuPage;


我的理解:
let add1 = x => y => z => x + y + z //add1 = (x)=>{ return (x)=>{ (y) => { (z) => { x + y + z } } } }
let add2 = add1(1) //add2 = (y)=>{ return (y)=>{ (z) => { 1 + y + z } } }
let add3 = add2(2) //add3 = (z)=>{ return 1 + 2 + z }
add3(3) //add3 = (3)=>{ return 1 + 2 + 3 }
function add1(x){
//此時add2能看到x,所以不用具體從參數帶入
function add2(y){
//此時add3能看到x,y,所以不用具體從參數帶入
return add3(z){
x + y + z
}
}
}
//=============================//
const logMiddleWare = store => next => action => {
console.log("dispatching", action);
next(action);
}
function logMiddleWare(store){
//此時Func1能看到store,所以不用具體從參數帶入
function Func1(next){
//此時Func2能看到store,next,所以不用具體從參數帶入
function Func2(action){
next(action);
}
}
}
//在Redux thunk中,Next其實可以當作dispatch
//在Redux thunk中,store其實可以當作State
//=======Redux thunk源碼========//
function createThunkMiddleware(extraArgument) {
// 這是 middleware 基本的寫法
return ({ dispatch, getState }) =>
(next) =>
(action) => {
// action 就是透過 action creators 傳進來的東西,在 redux-thunk 中會是 async function
if (typeof action === 'function') {
// 在這裡回傳「執行後的 async function」
return action(dispatch, getState, extraArgument);
}
// 如果傳進來的 action 不是 function,則當成一般的 action 處理
return next(action);
};
}
//=======在Redux thunk範例========//
// fetchTodoById is the "Thunk Action Creator"
export function fetchTodoById(todoId) {
// fetchTodoByIdThunk is the "Thunk Function"
return async function fetchTodoByIdThunk(dispatch, getState) {
const response = await client.get(`/fakeApi/todo/${todoId}`)
dispatch(todosLoaded(response.todos))
}
}
//use
function TodoComponent({ todoId }) {
const dispatch = useDispatch()
const onFetchClicked = () => {
// Calls the thunk action creator, and passes the thunk function to dispatch
dispatch(fetchTodoById(todoId))
}
}
//=======將範例套用到源碼中========//
function createThunkMiddleware(todoId) {
// 這是 middleware 基本的寫法
return ({ dispatch, getState }) =>
(dispatch) =>
(fetchTodoById) => {
// action 就是透過 action creators 傳進來的東西,在 redux-thunk 中會是 async function
if (typeof fetchTodoById=== 'function') {
// 在這裡回傳「執行後的 async function」
return fetchTodoById(dispatch, getState, todoId);
}
// 如果傳進來的 action 不是 function,則當成一般的 action 處理
return dispatch(fetchTodoById);
};
}